What is Rayon (Breathable Fabric)? Types And Care
Curious about what rayon is and its place in the fabric world? This guide demystifies rayon, explaining why it’s a versatile semi-synthetic fiber derived from natural cellulose. You’ll learn about its desirable properties like softness, breathability, and excellent drape, often making it feel similar to silk or cotton.
Discover the different types including Viscose, Modal, and Lyocell, their common uses in clothing and home goods, and essential care instructions to keep your rayon items looking their best. Gain a comprehensive understanding of this popular textile.
1. What exactly is rayon?
Rayon is a manufactured fiber, which means it’s made by people. But, it starts from something natural: cellulose. Cellulose is like the main stuff inside plants, especially from wood pulp – think of tiny bits from trees.
Because it starts natural but needs chemicals and machines to become fiber, we call rayon ‘semi-synthetic’. It’s like it’s halfway between natural fabrics (like cotton) and fully man-made fabrics (like polyester). Think about paper. It comes from trees (natural), but it takes a process to turn wood into paper sheets. Rayon is similar – wood pulp needs a process to become fabric threads.

2. How is rayon made?
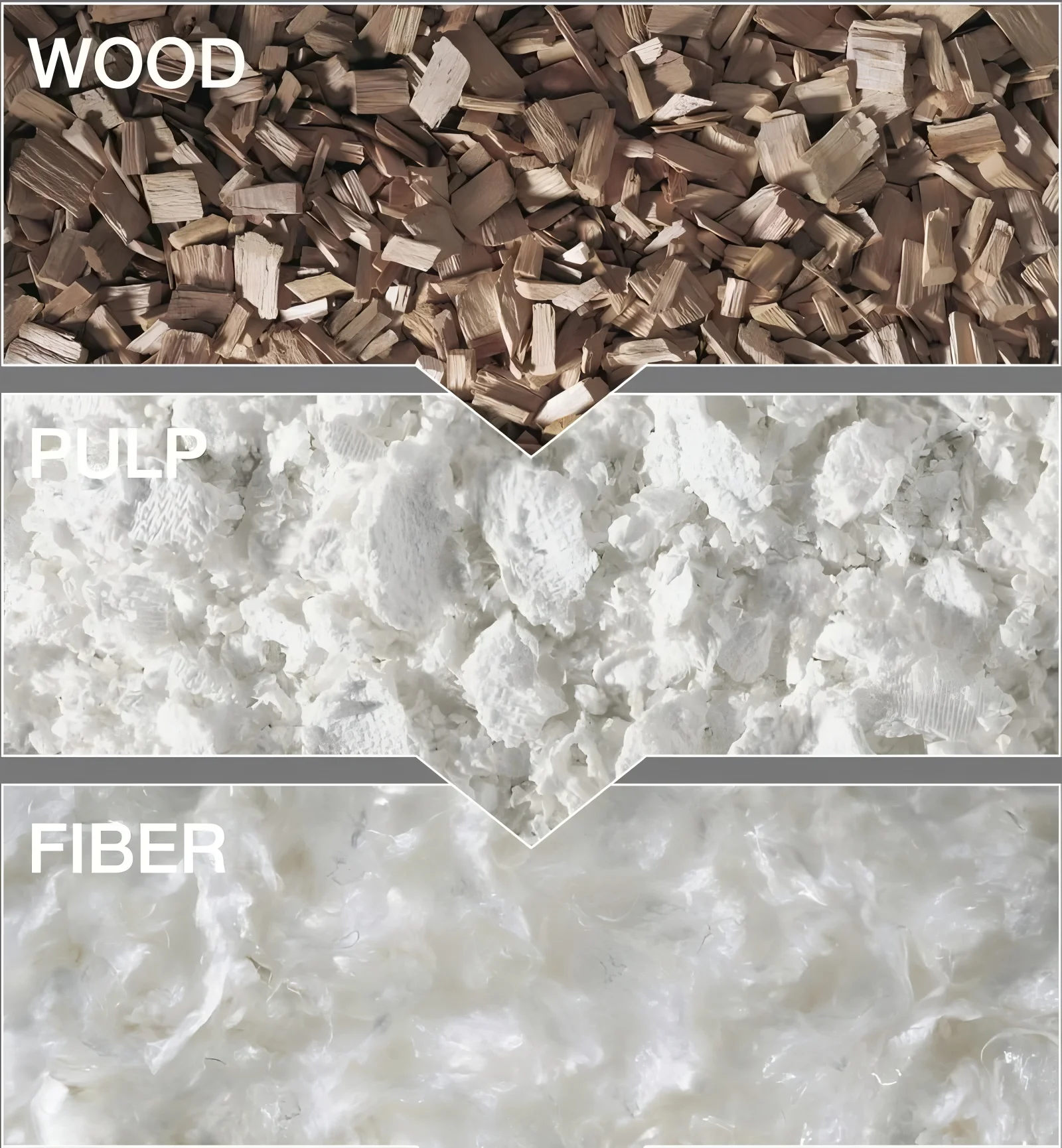
So how does wood turn into fabric? Here’s a very basic idea:
- Start with wood pulp (cellulose).
- Mix it with chemicals to dissolve it into a thick, syrupy liquid. (This liquid is sometimes called ‘viscose’). This is part of the viscose process.
- Push this liquid through tiny holes, like a showerhead, into another chemical bath. This makes the liquid harden into thin threads (fibers).
- These threads (now rayon fibers, a type of regenerated cellulose fiber) are spun together to make yarn. Then, the yarn is woven or knitted to make the rayon fabric we use.

3. What does rayon feel and act like?
What is rayon like when you wear it or touch it? Here are the main properties and characteristics of rayon:
- Softness: Rayon usually feels very soft and smooth on your skin. It can feel a bit like silk or soft cotton. People used to call it ‘Artificial Silk’.
- Drape: It has good drape. Drape means how the fabric hangs or falls. Rayon often hangs nicely, making clothes look flowy and elegant.
- Absorbency: Rayon is very absorbent. It has high absorbency, meaning it soaks up water (and sweat) well. This helps you feel more comfortable in warm weather because it doesn’t trap moisture against your skin like some synthetic fabrics.
- Breathability: It’s also breathable. Air can pass through it easily. This helps keep you cool.
- Versatility: Rayon is versatile. It can be made to look and feel like other fabrics, such as cotton, linen, or wool. Its versatility is why you find it in so many different types of clothes.
- Some downsides: Rayon can wrinkle easily. Also, it can sometimes get weaker when it’s wet, and it might shrink if you don’t wash it carefully. (We’ll talk more about washing later!)
4. Are there different kinds of rayon?
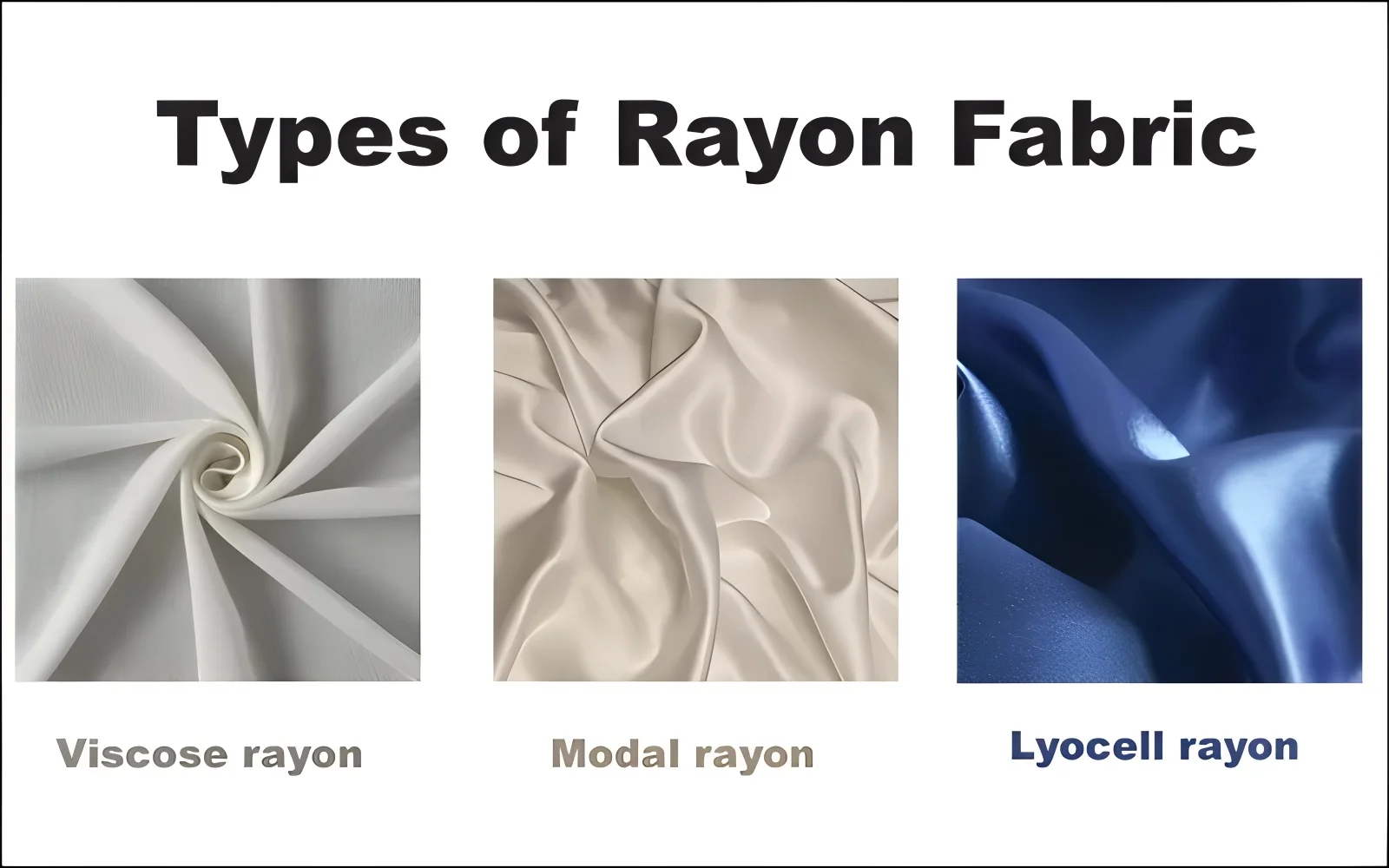
Yes, there are a few main kinds of rayon you might see on labels. Here are the different types of rayon explained:
- Viscose rayon: This is the most common type. Often, when people just say ‘rayon’, they mean Viscose. It’s made using the process we talked about earlier (with the ‘viscose’ liquid).
- Modal rayon: Modal is often softer than regular viscose. It’s also stronger when wet, which is helpful. You often find modal rayon in things like underwear, pajamas, and towels.
- Lyocell (Tencel is a brand name): Lyocell is another type. It’s made using a process that’s kinder to the environment. It’s strong, soft, and doesn’t wrinkle as easily as other rayons. You might see the brand name Tencel on labels; Tencel is a popular brand of Lyocell.
5. Where do we use rayon? Common uses
You can find rayon fabric in many things you use every day, especially in the apparel industry and for home furnishings.
- Clothing: Rayon is very popular for clothes because it’s soft and hangs nicely. Examples include dresses, blouses, skirts, casual shirts, t-shirts, linings for jackets and suits, and comfortable trousers or pajamas.
- Home Items: It’s also used around the house. Examples: Bed sheets and blankets, Curtains, Sometimes in furniture covers.
6. Taking care of your rayon items
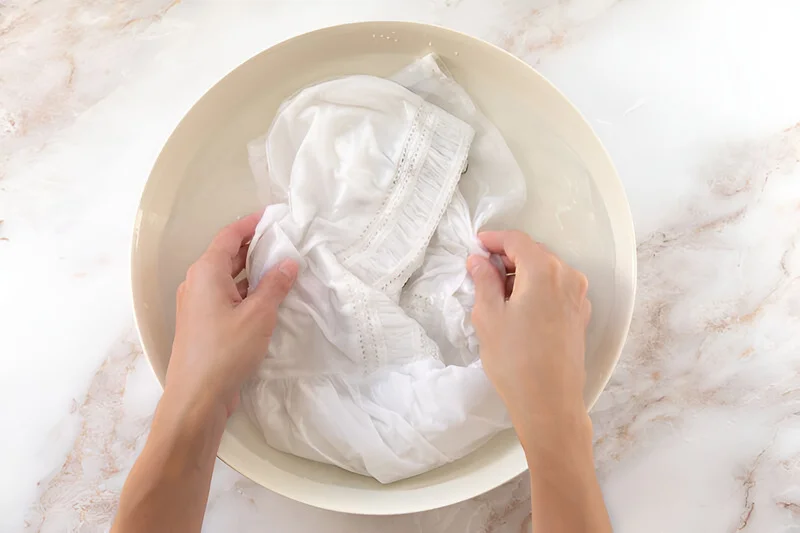
Knowing how to care for rayon clothing is important. Does rayon shrink? Yes, it can if not cared for properly. Here’s how to wash and care for rayon garments:
- Always check the care label first! Different rayon items might need different care.
- Washing: It’s usually best to be gentle. Hand wash in cold water if you can. If using a machine, choose the delicate cycle with cold water. Putting the item in a mesh laundry bag can help protect it. This helps prevent shrinking and damage, as rayon can be weaker when wet. So, wash rayon gently.
- Detergent: Use a mild soap or detergent.
- Heat is bad: Avoid hot water and high heat dryers. Heat can make rayon shrink or get damaged.
- Drying: Air dry is usually best. Lay the item flat on a clean towel or hang it on a padded hanger (avoid clips that can stretch it). Do not put rayon in a hot tumble dryer unless the label clearly says you can. Learning how to dry rayon properly prevents damage.
- Ironing: If you need to iron rayon, use the lowest heat setting (often labeled ‘rayon’ or ‘silk’). It helps to iron when the fabric is still a little damp, or iron on the inside-out (‘reverse’) side. You can also put a thin cloth (called a pressing cloth) between the iron and the rayon.
- Dry Cleaning: Sometimes the label will say ‘Dry Clean Only‘. If so, follow that instruction.

7. Questions about rayon
7.1 Is rayon an environmentally friendly fabric choice?
Rayon’s environmental impact is complex. On one hand, it originates from a natural, renewable resource – wood pulp (cellulose) – and is biodegradable under the right conditions. This gives it an advantage over fully synthetic, petroleum-based fabrics like polyester.
However, the traditional manufacturing process for viscose rayon (the most common type) can involve harsh chemicals and significant water usage, which can be detrimental if not managed responsibly.
Newer types like Lyocell (often under the Tencel™ brand) utilize more closed-loop processes that recycle water and chemicals, making them a much more sustainable and eco-friendly rayon option.
7.2 How does rayon’s cost compare to other common fabrics?
The cost of rayon fabric can vary significantly depending on the specific type and quality. Generally, basic viscose rayon is often quite affordable, sometimes comparable to or even less expensive than cotton, and often cheaper than many polyesters, making it a popular choice for budget-friendly fashion.
More specialized rayons, such as Modal or Lyocell (especially branded versions like Tencel™), tend to be more expensive. This higher price reflects their enhanced properties like superior softness, increased strength (especially when wet for Modal), better wrinkle resistance, and often more sustainable manufacturing processes.
7.3 Can rayon be blended with other fibers, and what are the benefits?
Yes, rayon is frequently blended with other fibers to enhance its properties or achieve specific characteristics in the final fabric. Common blending partners include cotton, polyester, and spandex (elastane).
For instance, blending rayon with cotton can improve strength and add a more familiar texture. When mixed with spandex, rayon gains stretch and recovery, making it ideal for comfortable, form-fitting garments. Blending with polyester can help reduce rayon’s tendency to wrinkle and can improve the overall durability and affordability of the fabric.
7.4 What are the main differences between Viscose, Modal, and Lyocell rayon?
While all types of rayon are known for their softness, there are noticeable differences. Standard viscose rayon is the most common and generally feels soft and silk-like, but it can be weaker when wet and more prone to shrinking and wrinkling.
Modal rayon is often considered an improved version, typically feeling even softer and silkier than viscose, and it boasts better strength when wet and greater resistance to shrinking and pilling.
Lyocell (often seen under the Tencel™ brand) generally offers the highest performance, combining excellent softness and smoothness with good strength (both wet and dry), better wrinkle resistance, and a more sustainable production profile.
7.5 Why does rayon sometimes have a ‘chemical’ smell when new, and does it go away?
A slight ‘chemical’ odor in new rayon garments can sometimes occur due to residues from the chemicals used in the manufacturing or finishing processes. This is more common in some types of viscose rayon where the chemical processing is more intensive.
Fortunately, this smell is usually not permanent and typically dissipates after the garment has been aired out for a period or after its first wash according to the care label instructions. Washing helps to remove any lingering surface residues, leaving the fabric fresh.
Explore more:
So, that’s rayon in simple terms! It’s a semi-synthetic fiber made from plant cellulose. It’s known for being soft, absorbent, and hangs well (good drape). You’ll find it in countless clothing and home items, making it one of the most versatile and common fabrics available today. Just remember to check the label and wash it gently! Now you know the basics about this common fabric!






















